What is IPM?
Modern IPM frameworks now integrate economic viability, environmental safety, and social acceptability, ensuring that pest management aligns with broader sustainability goals.
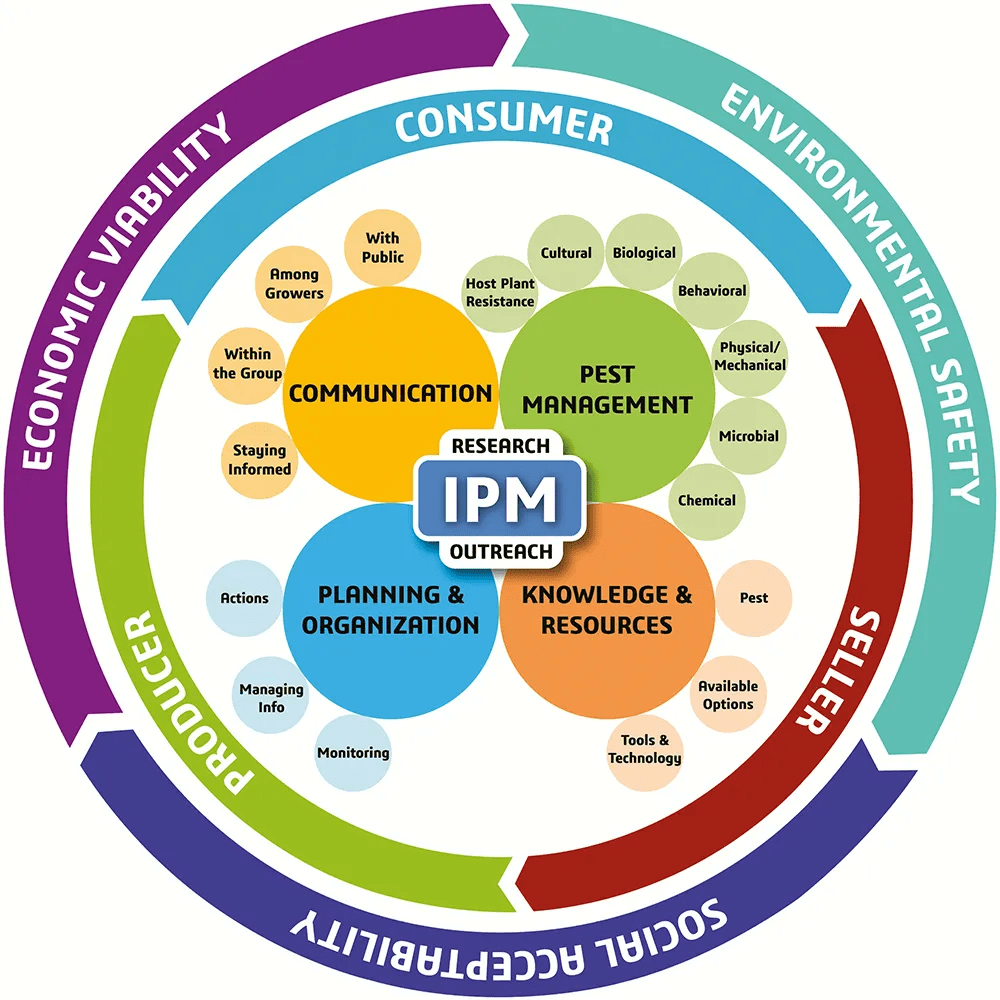
The New Integrated Pest Management Paradigm for the Modern Age
How IPM Works

Monitoring & Identification
Regular field scouting helps detect pest and disease threats early. Advanced monitoring technologies, such as remote sensing and automated data collection, further enhance early detection and support better decision-making.

Prevention

Biological Control

Mechanical Control
Employing traps, barriers, and mechanical removal helps limit pest spread, while new innovations like temperature treatments and light-based trapping systems target specific pests while preserving beneficial organisms.

Chemical Control

Cultural Control
Andermatt Biological Solutions
Benefits of IPM

Reduced Chemical
Dependence

Improved Soil
and Plant Health

Sustainability and
Environmental Protection

Resistance
Management
Implementing IPM reduces the risk of pests developing resistance by combining multiple control strategies. By integrating different approaches, IPM slows down resistance evolution and helps preserve the effectiveness of pest control tools over time.

Cost-Effective
Farming

Enhanced Crop Quality
and Yield
Integrating Biologicals into Traditional Farming
Selecting the right biological agents that complement traditional methods.
Timing applications to align with pest lifecycles for maximum efficacy.
Ensuring compatibility with existing spray programs and farming practices.
Educating farmworkers on correct application, storage, and monitoring.
Why Choose IPM?
Reduce chemical use while maintaining effective pest control.
Protect biodiversity and natural ecosystems.
Increase profitability through sustainable practices.
At Andermatt Madumbi, we are committed to supporting farmers in developing an IPM strategy tailored to their unique needs.
Let’s work together towards a more sustainable future for agriculture!
References
The New Integrated Pest Management Paradigm for the Modern Age
